6.2 Which antibiotics are most effective against Ileitis?
The minimum inhibitory concentrations of various antibiotics against laboratory cultures of Lawsonia intracellularis have been examined in several studies (see Table 6.2 a). However, experience has shown that the actual effect of each drug in animals is of more value in determining which antibiotics to recommend for this disease than results in the test tube. In Lawsonia intracellularis challenge studies controlled evaluations of the therapeutic efficacy of tiamulin, tylosin and lincomycin were measured. These three drugs have shown to be effective against Lawsonia intracellularis. It is possible that these drugs concentrate in the enterocytes infected with Lawsonia intracellularis.
Not all antibiotics are effective against each disease. Several antimicrobial active substances which have not proved fully effective in Ileitis challenge situations include the growth promoters bacitracin, virginiamycin and salinomycin. Penicillins, aminoglycosides and the fluoroquinolones have proven ineffective in trials. Some of these drugs (the growth promoters) are not effective because they are aimed at the Gram-positive bacteria, while the others do not seem to target the correct tissues and cell location of Lawsonia intracellularis.
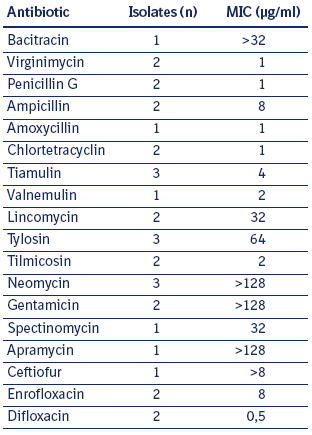
Table 6.2 a
Antimicrobial activity
against Lawsonia intracellularis.
© Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health GmbH, 2006
All rights reserved. No part of this Technical Manual 3.0 may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or photocopy, without permission in writing from Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health GmbH.






