



Determination of Minimal Inhibition Concentrations of Major Antibiotics for Strep suis
FRANCE - Amoxicillin is the optimal choice for the first line treatment and control of Streptococcus suis infections in pigs, report P. Butty and R. Krejci of Ceva in Libourne.Streptococcus suis belongs to the most frequent bacterial pathogens in pigs raised in industrial farms.
It is a primary pathogen, inducing disease often associated with septicaemia, meningitis, pneumonia, arthritis and endocarditis, which can be often fatal.
Sick animals should be treated as soon as possible with antibiotics. All pigs in a group should be treated when a single pig becomes clinically ill.
Amoxicillin is the antibiotic of the first choice in the treatment and control of S. suis infections1.
The aim of this study was to compare the susceptibility of S. suis to amoxicillin (AMX) and other frequently used antibiotics in swine, namely ceftiofur (CEF) and marbofloxacin (MAR).
Materials and Methods
A total of 94 S. suis isolates were collected from clinically ill pigs from French (Labofarm) and German Veterinary Laboratories during the years 2009 and 2010. The strains were sub-cultured twice on five per cent sheep blood Colombia agar (35°C for 16 to 18 hours) prior to MIC testing. MICs were determined for each antibiotic, using the micro-dilution method of the NCCLS.
Results
All strains of S. suis isolates were 100 per cent sensitive to all three antibiotics. However differences in the MIC 50 and MIC 90 were found between AMX, CEF and MAR (Figure 1).
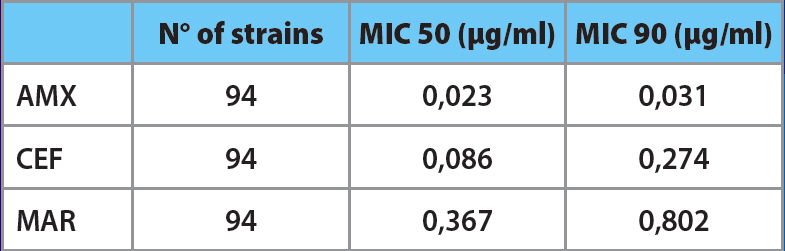
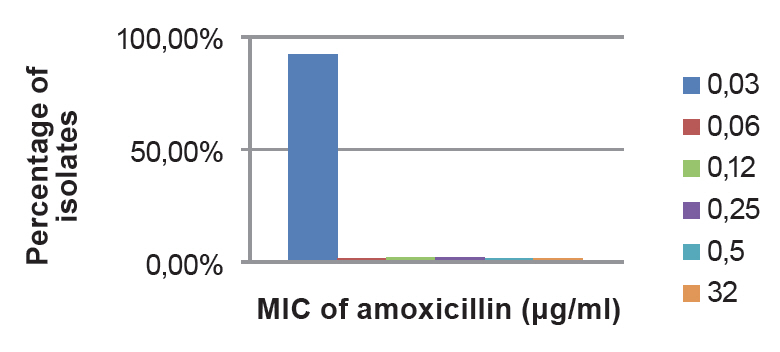
The distribution of particular MICs for S. suis showed 92.2 per cent strains susceptible to 0.03μg per ml of AMX (Figure 2).
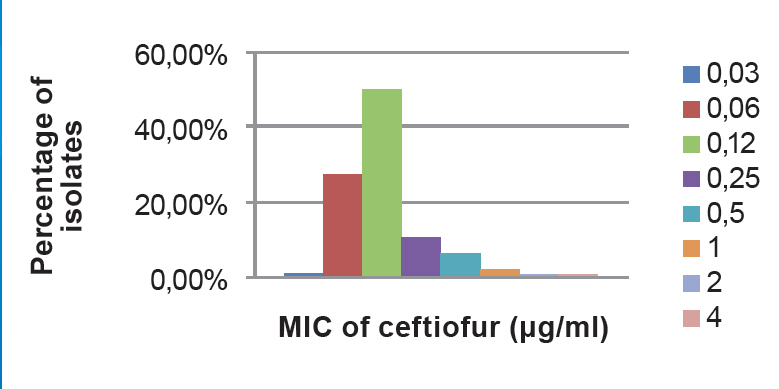
50 per cent of isolates were susceptible to 0.12μg per ml of CEF (Figure 3).
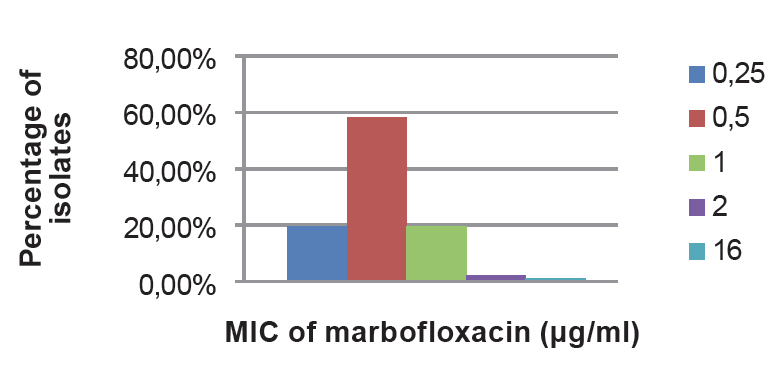
58 per cent strains were susceptible to 0.5μg per ml of MAR (Figure 4).
CLSI Clinical break-point for AMX is <0.25; >8μg per ml, and for CEF: <2; >8μg per ml.
There is no CLSI clinical break-point for MAR.
Conclusion
Amoxicillin was the most efficient antibiotic against S. suis isolates among the three major molecules examined in this study with 92 per cent of isolates being susceptible to the lowest concentration.
This confirms that amoxicillin is still the optimal choice for the first line treatment and control of S. suis infections in pigs.
Bibliography
- Gottschalk, AASV, 2002
- NCCLS, M31-A3, Vol28 N°8-2008







