5.1.2 Immunofluorescence assay (IFA) for the detection of antibodies against Lawsonia intracellularis
Principle of the test:
Continuous cell lines infected with Lawsonia intracellularis are fixed on 96 well microtiter plates or on test slides that serve as the antigen template. Serum samples diluted 1 to 30 are incubated with the template to indicate positive or negative results. Serial dilutions of sera can be used to determine the antibodies. The binding of Lawsonia intracellularis specific antibodies to the antigen template is detected by a fluorescence labelled anti-species specific secondary antibody (for example: goat anti swine FITC conjugated). Three positive sera (high, medium and low) and a negative serum serve as controls.
Special equipment:
Immunofluorescence is evaluated using an UV microscope. An inverted microscope is used in case of 96 well microtiter plates.
Result format:
Test results are given as positive, negative or questionable. Unspecific staining is mentioned as negative.
Positive reactions with dilutions ≥ 1 in 30 are determined according the method of Spaerman and Kaerber. Dilutions less than 1 in 30 may lead to unspecific staining, which does not allow a clear interpretation.
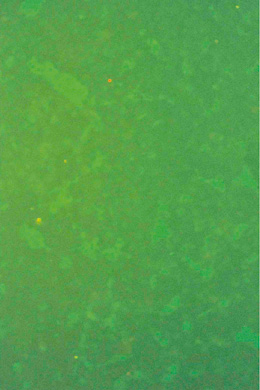
Picture 5.1.2 a
No specific immunofluorescence with
negative serum from swine.
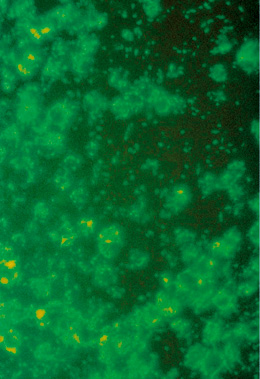
Picture 5.1.2 b
Lawsonia intracellularis specific staining with post infection serum from swine. Lawsonia intracellularis can be detected intracellularly, at the cell membranes, or as non cell associated
bacteria. Magnification: 160 x.
© Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health GmbH, 2006
All rights reserved. No part of this Technical Manual 3.0 may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or photocopy, without permission in writing from Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health GmbH.






