



Common sense evaporative cooling
As hot outside air moves through wet cool cell pads, it loses heat by evaporating the water. The heat isn't destroyed but instead changes to another form, water vapor. So the incoming air is now cooler but its humidity has also increased. The drier the air, the more potential cooling is possible. 90° air with 20% humidity has the potential to be cooled to 67°, while the same 90° air with 60% humidity has only the potential to drop to 86°. Evaporative cooling will only lower the felt temperature so far depending on the air's humidity.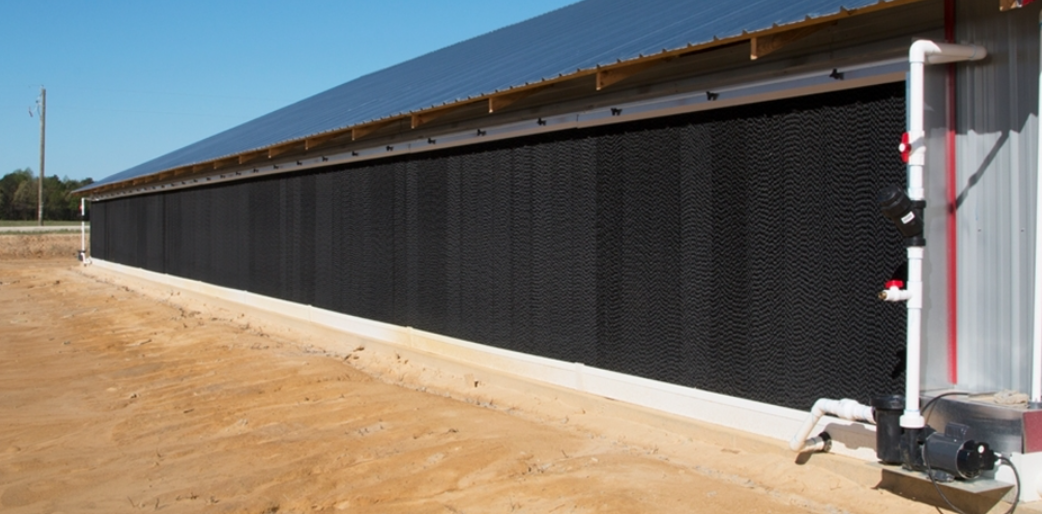
The 80-80 rule
Does this mean evaporative cooling is only effective in a desert-like climate with low humidity? The 80-80 rule answers this question. The August 2000 edition of Poultry Housing Tips (Czarick and Lacy, 2000) highlighted data showing when the temperature is above 80° F the humidity level will almost always be below 80%. The graph in Figure.1 shows the relationship between relative humidity and temperature.
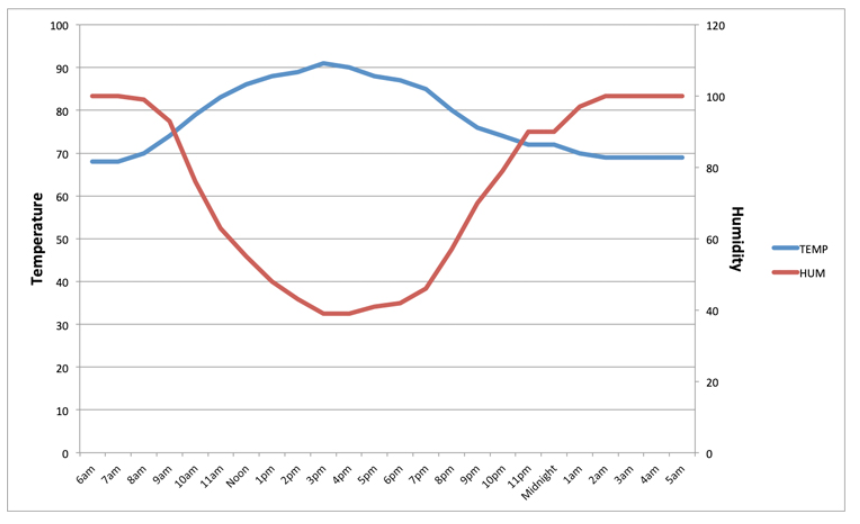
On a typical 70° summer morning with heavy dew on the ground, there is minimal cooling that will result from running the evaporative cooling system. As temperatures reach 80° by midmorning, the humidity drops below 80%, and evaporative cooling is now effective. The same holds true in the evening; as the temperature cools to below 80°, the humidity will rise above 80%, diminishing the evap system’s effectiveness. It is difficult to evaporate additional water when the air is already saturated. Typically there is very little value in operating a cool cell system between 10 pm and 10 am as a general rule.
Dry the pads out
Some producers operate their system with the idea that even a little cooling is beneficial, so why not run the pads continuously? Not allowing the evaporative pads to dry each day will severely shorten their useful life. Think of it this way - evap pads are a treated paper product. If you let a cardboard box stay wet, it will eventually collapse and lose its shape. If that same box dries out each day, it will keep its form much longer. Same with cool cell pads. A five-foot pad weighs about 5-1/2 pounds dry. When it is fully saturated, it could easily double in weight. The extra weight causes the pads to fail structurally over time. The more time a pad spends with this extra weight, the quicker it fails. Allowing the pads to dry each night between 10 pm and 10 am extends their useful life.
Airspeed is key
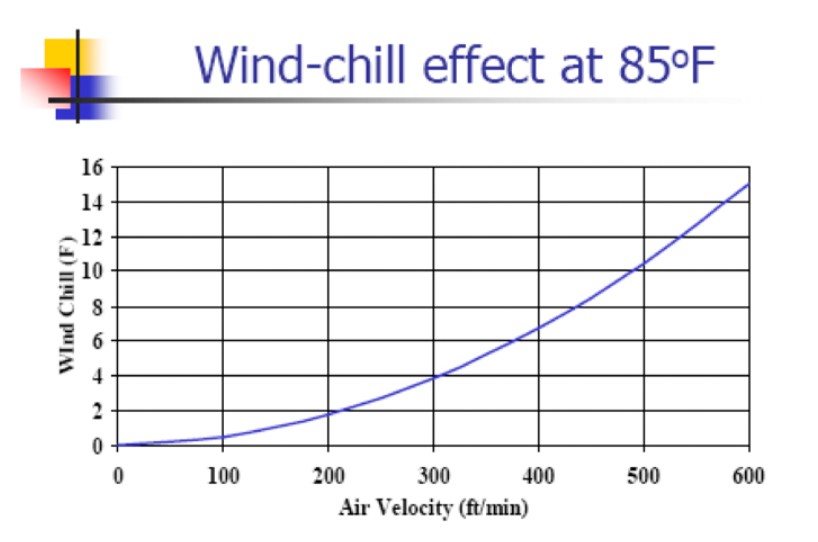
The evaporative pads are only part of the cooling system. The key to maximizing the effectiveness of an evaporative cooling system is moving air at high velocities with tunnel fans. Going back to our earlier example of the 70° summer morning with high humidity highlights this principle. If there is a breeze blowing, the temperature seems pleasant. If the wind is calm, the weather feels hot and muggy. The graph in Figure 2 illustrates the wind chill effect of 85° F air at various wind speeds. 85°air feels like 75° air when it is moving at 500 feet per second. It does little good to operate an evaporative cooling system without adequately designed and maintained tunnel fans delivering sufficient airspeed.
There is no mystery to operating an evaporative cooling system effectively. You can observe the environment around you to make some common sense choices on how that system performs.






